Cannabis Education: Anything worth trying is worth learning about.
Any reservations?
Have questions on whether or not cannabis is right for you?
Need to know what kind of cannabis would work best to help treat different conditions?
Look no further! We have assembled a variety of different facts and information related to cannabis on this page so if you are new to our community or are just trying to understand cannabis more we hope what we have here will assist you and answer some of the most common questions. It is always best to speak to a budtender regarding cannabis information but we understand not everyone here has access to our storefront and online information is far easier to access.
THE BASICS
Marijuana, also known as cannabis or pot, has a long history of human use. Most ancient cultures didn’t grow the plant to get high, but as herbal medicine, likely starting in Asia around 500 BC. The history of cannabis cultivation in America dates back to the early colonists, who grew hemp for textiles and rope. Political and racial factors in the 20th century led to the criminalization of marijuana in the United States, though its legal status is changing in many places.
The cannabis or hemp plant originally evolved in Central Asia before people introduced the plant into Africa, Europe, and eventually the Americas. Hemp fiber was used to make clothing, paper, sails, and rope, and its seeds were used as food.
Because it’s a fast-growing plant that’s easy to cultivate and has many uses, hemp was widely grown throughout colonial America and at Spanish missions in the Southwest. In the early 1600s, the Virginia, Massachusetts, and Connecticut colonies required farmers to grow hemp.
These early hemp plants had very low levels of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the chemical responsible for marijuana’s mind-altering effects.
There’s some evidence that ancient cultures knew about the psychoactive properties of the cannabis plant. They may have cultivated some varieties to produce higher levels of THC for use in religious ceremonies or healing practices.
Burned cannabis seeds have been found in the graves of shamans in China and Siberia from as early as 500 BC.
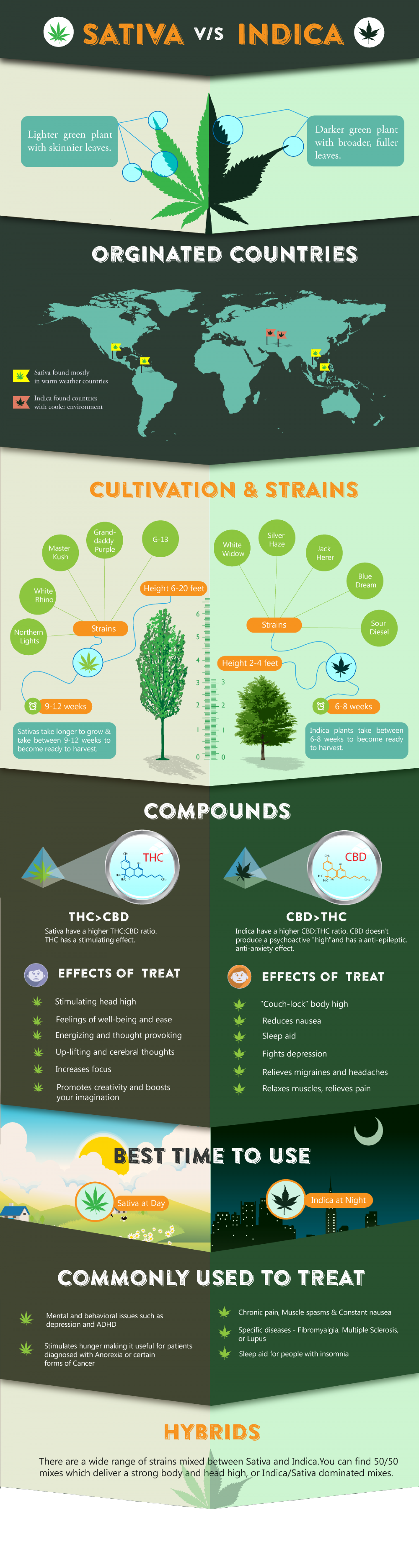
Who’s Who? (Sativa vs. Indica)
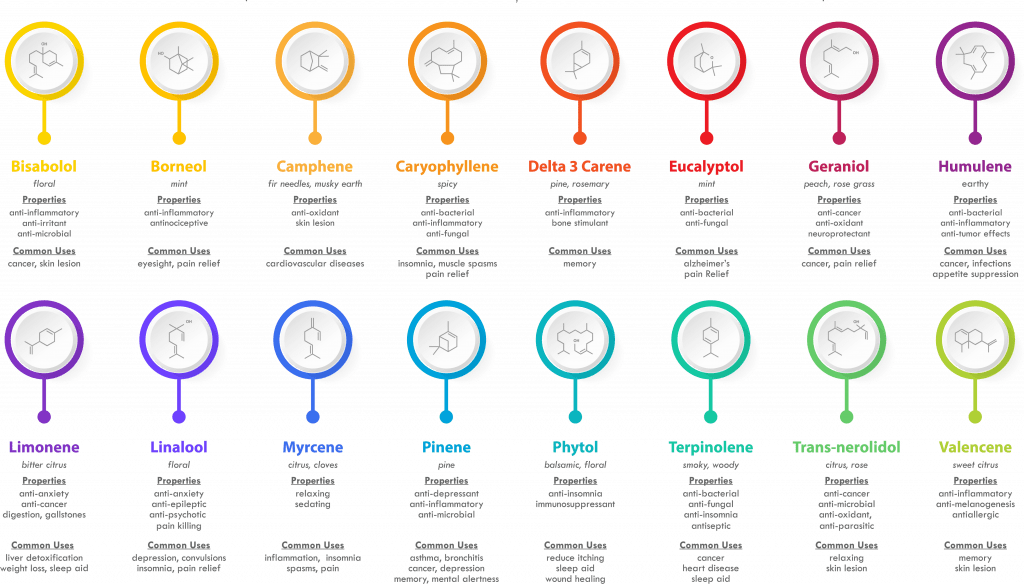
Terpenes are your best friend in Cannabis
You already know what terpenes are because you’ve experienced them all your life. Simply put, terpenes are what give an orange its citrusy smell. They give pine trees their unique aroma. They’re even responsible for the relaxing effects of lavender. They are chemicals that determine how things smell.
You can find terpenes in most plants and foods. In fact, if you look back at what you ate today you more than likely ate something containing one or more terpenes in them.
So What are Terpenes?
Terpenes are highly aromatic compounds that determine the smell of many plants and herbs, such as rosemary and lavender, as well as some animals.
Manufacturers use isolated terpenes to create the flavors and scents of many everyday products, such as perfumes, body products, and even foods.
Terpenes play a vital role in plants. In some plants, terpenes attract pollinators, while in other plants, they cause a strong reaction to repel predators, such as insects or foraging animals.
Some terpenes play a protective role in the plant, helping the plant to recover from damage; others act as a part of the plant’s immune system to keep away infectious germs.
Some people also use the term terpenoids. However, terpenes and terpenoids are not the same.
Terpenes are the natural form of these compounds when they are in the live plant. As a plant dries and cures — in the production of cannabis, for example — the terpenes oxidize and become terpenoids.
So if you weren’t entirely sure what Terpenes were hopefully we have been able to increase your insight into them a bit. To understand how they work in Cannabis we must first understand what Cannabinoids are.
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids — the active chemicals in medical marijuana — are similar to chemicals the body makes that are involved in appetite, memory, movement, and pain.
Research suggests cannabinoids might:
• Reduce anxiety
• Reduce inflammation and relieve pain
• Control nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy
• Kill cancer cells and slow tumor growth
• Relax tight muscles in people with multiple sclerosis
• Stimulate appetite and improve weight gain in people with cancer and AIDS
In short; your brain already has Cannabinoid receptors inside it, when you intake THC in cannabis you overload your Cannabinoid receptors in your brain giving you the desired effect or as it\'s commonly known as being High, Stoned, or Baked.
Still with us?
Okay, Great! Now let’s talk about how Terpenes work with cannabis and go over the main types and effects of terps in cannabis.
Currently, there are at least 20,000 different terpenes in existence and the cannabis plant has more than 100 of these terpenes. Many terpenes that are produced by the cannabis plant are also found elsewhere in nature. However, there are a couple of terpenes that are in high concentrations in cannabis plants. Here are the main ones to know.
Is more THC Better?
“”I want the highest percent you have”
Is one of the most common and one of the more frustrating questions budtenders receive, no we are not sorry.
The annoyance in our state comes from the fact that we as a company deal with a lot of medical patients with actual medical needs for cannabis. When people come in asking for the highest THC percent in flower that we have it is frustrating for a few reasons:
1. It makes you appear Uneducated, and that’s not a bad thing. There are a lot of new people obtaining medical patient licenses every day that are entirely brand to this entire world of Cannabis. After all, it makes sense that something with higher THC should produce stronger effects right? Well, yes and no. THC does have its place in the topic of strain potency, however, in simple terms, it acts as a vessel for the effects the Terpenes produce.
2. It takes away from the medical focus. In our state as of early 2020, it is only available to medical patients and our state has a strong emphasis on medical use. When customers come in and ask for the highest THC content our budtenders notice it as people wanting cannabis for recreational use rather than the medical purpose that our state currently intends it for. That’s not a bad thing but as a state with an emphasis on the medical aspect, people are still wary of the recreational side of cannabis.
Terpenes are your friend and the higher the terpenes, the stronger the desired effects will be.
CBG is relatively new in the realm of studied endocannabinoids, By now, most people familiar with cannabis have heard of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) and their effects, but did you know there are many similar compounds in cannabis? A lesser-known cannabinoid called cannabigerol (CBG), while not present in large quantities in most strains, is nonetheless worth learning about for a number of reasons.
Our body contains two types of cannabinoid receptors—CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are found in the nervous system and brain, while CB2 receptors are located in the immune system and other areas of the body. CBG works by binding to both receptors where it’s thought to strengthen the function of anandamide, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in enhancing pleasure and motivation, regulating appetite and sleep, and alleviating pain. Unlike THC, CBG has no psychotropic effects, so it will not give you a high.
CBG has been found to act on very specific physiological systems and problems, and results for medicinal use are promising:
• Endocannabinoid receptors are prevalent in eye structures, and interestingly, CBG is thought to be particularly effective in treating glaucoma because it reduces intraocular pressure. It is a powerful vasodilator and has neuroprotective effects to boot.
• CBG is showing great promise as a cancer fighter. Specifically, CBG was shown to block receptors that cause cancer cell growth. In one such study, it was shown to inhibit the growth of colorectal cancer cells in mice, thereby slowing colon cancer growth. CBG inhibited tumors and chemically-induced colon carcinogenesis, therefore demonstrating a very exciting possibility for a cure for colorectal cancer.
• In a study that looked at the effects of five different cannabinoids on bladder contractions, CBG tested best at inhibiting muscle contractions, so it may be a future tool in preventing bladder dysfunction disorders.
CBG is often compared to CBD because it shares many similarities and they both act on the endocannabinoid system. Both CBG and CBD are non-psychoactive which means they will not alter your state of mind in the way THC will. They can however reduce the psychotropic effect of THC if you consume a cannabis plant. One of the biggest differences between CBD and CBG is the quantity that is found in most cannabis plants. Most cannabis plants contain only 1% of CBG, but up to 25% of CBD.
The way CBG interacts with our endocannabinoid system is different from CBD. CBG binds directly to both CB1 and CB2 receptors and might be more efficient at delivering its benefits into our systems.
There are a lot of potential medical benefits to be had from CBG, despite its scarcity we have started to notice more growers paying more attention to their CBG percentages, there is still a lot of science to be done with CBG as it is still relatively new but this is a very valuable cannabinoid nonetheless
CONCLUSION
When shopping for strains we recommend looking into the different terpenes in cannabis to find which will have the effects you are looking for. So we
recommend finding the perfect balance between THC potency and terpene potency.
So for example something with 17% THC and 2% Terpenes Vs. 30% THC and 0.5% terpenes means that even though there is a higher level of THC potency in one strain, the other strain with higher terpenes would most likely have stronger effects due to the higher amount of terpenes present.
Keep in mind that everyone is different so cannabis strains may affect you differently than your friend, family member, or budtender.
Check back for updates!
We are always making adjustments and improvements as changes and new information is presented. a very valuable cannabinoid nonetheless
